Introduction
Pneumatic cylinders are useful parts of many machines and are powered by compressed air to work. These devices are used in various industries, such as manufacturing, packaging, etc. In this post, we will explore the principles of operation of pneumatic cylinders, their different types and uses, and the benefits they offer in automation. Having an understanding of these components will help you make better decisions related to your projects, and thus improve your operational efficiency.
What are Pneumatic Cylinders?
Pneumatic cylinders also known as air cylinders are devices that use compressed gas energy to create linear motion. Basically compressed air drives a piston that is inside a cylinder, and the piston moves in linear motion by pushing or pulling.
Working Principle or Functionality
Pneumatic cylinder Components
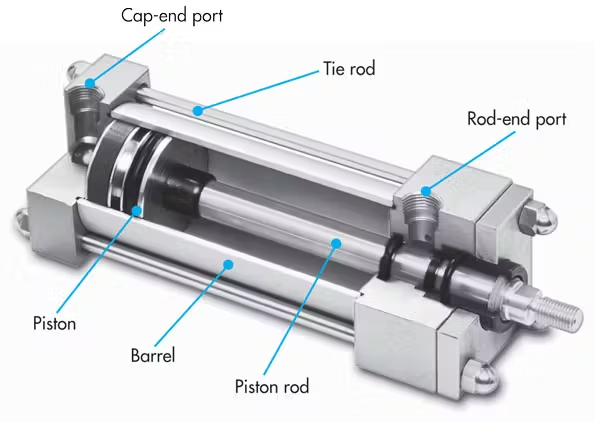
- Cylinder body: This is the outer framework that contains the internal parts and provides stability.
- Piston: A cylindrical or disc-shaped component that rotates within the cylinder body. It is responsible for transmitting the force generated by compressed air.
- Piston rod: A metal rod attached to the piston, which extends outside the cylinder. It transfers the linear motion of the piston to the load.
- Air inlet and outlet ports: These ports allow compressed air to enter and exit the cylinder, controlling the movement of the piston.
- Seal: A sealing mechanism prevents air leakage between the piston and the cylinder wall.
- End caps: These components seal the ends of the cylinder and provide mounting points.
How Pneumatic cylinders Work
Pneumatic cylinders are machines that use compressed air and provide linear motion. Because they are very simple, reliable, and versatile, they have wide application in many industries.
- Air supply: Compressed air is supplied to the cylinder from an external source, such as an air compressor.
- Air inlet: Compressed air enters the cylinder chamber through the inlet port.
- Piston movement: Air pressure forces the piston to move in a specific direction, either extending or retracting.
- Load application: The piston rod attached to the piston transmits linear motion to the load, causing the desired work.
- Air exhaust: As the piston moves, the air in the opposite chamber is exhausted through the outlet port.
Types of Pneumatic Cylinders
Pneumatic cylinders are versatile devices that convert compressed air energy into linear motion. While they share a common principle of operation, they come in a variety of types, each of which is suitable for specific applications. Here is a description of the most common types:
- Single-acting cylinders: Single acting cylinders have the most basic configuration of all pneumatic cylinders, they have one air port and operate in only one direction which is usually an extension stroke. In most cases there is a spring. They are ideal for simple processes such as turning a switch on and off or controlling a valve.
- Double-acting cylinders: Double-acting cylinders are superior to single-acting cylinders. Since they have two ports that allow for both extension and retraction strokes, they can be used in a wide range of applications such as automating tasks involving robotics, material handling, and more.
- Telescopic cylinders: Telescopic cylinders are designed with more compact dimensions but have a longer stroke length. Their design includes multiple stages that allow them to be extended one at a time and so they are useful in applications requiring long strokes but suffer from space limitations. This makes them suitable for heavy-duty applications such as lifting and positioning heavy loads.
- Rodless Cylinder: Rodless cylinders are a special type of pneumatic actuator that can be called space-efficient, and in this case, they can be called space-efficient and they do not use a standard piston rod. Instead, they use a magnetic or mechanical coupling that provides the force to the load. This construction eliminates the rod seals which reduces frictional forces and improves performance. However the rodless cylinder design is best for systems with limited space, where contamination may be a concern or where a long stroke length is required.
Other special types:
- Through-rod cylinder: This has a rod that passes through both ends of the cylinder, ensuring that force and speed are uniform in both directions.
- Cushion cylinder: This includes a built-in damping feature that reduces shock and vibration at the end of the stroke.
- Rotary cylinder: Enable rotational motion in the linear direction and are widely used in rotary indexing tables.
- Tandem cylinder: A set of two cylinders that are fixed longitudinally end to end to enable a longer stroke length.
Pneumatic cylinder Design and Manufacturing
Modern pneumatic cylinders are becoming more intelligent, more powerful and increasingly more functional across a variety of industries. They are also designed to be more compact and integrate seamlessly with automated equipment. So, let’s take a look at the constructional features of today’s industrial cylinders, the materials used in them, their installation methods and their relevance in today’s world.
Types of Pneumatic cylinder Construction
The design and construction of pneumatic cylinders is determined by their purpose. The following are some common types:
1. Tie Rod Cylinder:
- This is a common cylinder design that features great strength and protection.
- Aircraft cylinder cover plates contain tie rods that make this structure robust and suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- These are often plated to allow for better corrosion resistance and survival in aggressive environments.
2. Compact Cylinders:
- Designed for situations where space is a constraint.
- Have a significant force to size ratio making them suitable for use in automated systems with limited space.
- Mostly used in production lines that require power but in small sizes.
3. One-piece Welded Cylinder:
- Lowest cost, with welded or crimped ends, which makes this cylinder unsuitable in terms of servicing.
- These cylinders are easy to handle and can be used for primary operations which do not require much handling.
4. Threaded End Cylinders:
- Have threads at both ends, which are attached to the tube body with the help of screws.
- Although they are relatively light in weight, there may be some restrictions regarding their strength and stability.
5. Integrated-Sensor Cylinders:
- Sensors obtain information such as position, force, etc. in an automated manner.
- Recommended for applications requiring high accuracy as well as in combination with smart factory applications.
Materials Used for Pneumatic Cylinders
The material selected greatly affects the running and working life of the cylinder in extreme working conditions such as:
Aluminum is a common metal used in the manufacture of pneumatic cylinders because it is strong enough for a good strength-to-weight ratio. Stainless steel works well in low-stress applications and humid or high-moisture environments due to its high strength and durability. New composite resins and alloys improve the durability of parts and yet reduce weight. A large percentage of today’s pneumatic cylinders are manufactured from green and recyclable materials to reduce pollution.
Mounting options
The ease of installation and mounting of a pneumatic cylinder is influenced by its design, as it makes using the cylinder much easier. For horizontal mounts, foot mounts are common; for rotary units, clevis and trunnion mounts are used; for high-stress applications, flanged mounts are provided; and where cylinders need to be changed quickly, magnetic and quick-change mounts come in handy. Such modern fixing systems on pneumatic cylinders reduce idle time and increase operational efficiency in factories, making automation less difficult and managing pneumatically operated cylinders easier.
Cylinder Size
Depending on the application, pneumatic cylinders can be small, standard or large. Miniature examples are used when more precise movements are required for activities such as electronics and medical equipment handling. On the other hand, other examples are used in applications that require the lifting of heavy objects, such as moving materials.
Smart Technology Integration
Pneumatic cylinders are being equipped with intelligent technology features that include IoT and sensor integration to enable predictive maintenance as well as programmable logic control for precise movement of the cylinders. This makes the cylinders suitable for automated processes that require high precision.
Industrial Application of Pneumatic Cylinders
Due to their simplicity of maintenance, dependability, and efficacy, pneumatic cylinders can be found in almost all industries. They are able to convert compressed air energy into linear motion, which is fundamental in countless industrial uses. Below are several industries and applications where pneumatic cylinders are important:
1. Manufacturing and Assembly:
- Material Handling: In conveyor systems, pneumatic cylinders are used to lift, push or pull material in a production line.
- Clamping and Holding: These are used in assembly during processes such as welding, drilling or fastening by joining and holding parts together.
- Pressing and Stamping: These are widely used in metal working for punching, stamping and pressing materials into required forms.
2. Automotive industry:
- Automation of assembly lines: In particular, pneumatic cylinders control robot arms as well as automated systems that assemble vehicle parts.
- Lifting mechanisms: These are useful machines in assembly lines by lifting and positioning heavy automotive parts.
- Automatic door and hood test systems: The cylinders replicate the entire opening and closing movements of doors and hoods in durability testing.
3. Packaging Industry:
- Sorting and counting: The use of these cylinders makes it easier to sort, count and transfer items in packaging lines, making the production flow more efficient.
- Sealing and cutting: Shells are used in sealing machines for bags or packages, as well as, in machines that cut parts in paper or plastic packages.
- Bottle and container filling: Pneumatic cylinders make the entire process of filling, capping or even labeling bottles and other containers precise.
4. Food and beverage industry:
- Bottling and canning lines: Filling, sealing and labelling operations are controlled by pneumatic cylinders that guarantee hygiene and performance.
- Food processing machines: Used to cut, portion or pack foods.
- Automated sorting: Enables bulk sorting of foods as well as organisation and speed in mass production.
5. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Tablet Press Machines: This involves the use of machines that compress powders into tablets of specific dimensions in the manufacturing process.
- Packaging and Labeling: This involves the proper packaging and labeling of products which is important for correct compliance.
- Sterile and Controlled Environment: Speed and controlled environment are achieved by using pneumatic systems in sensitive areas to prevent hydraulic fluids from contaminating the area.
6. Textile Industry:
- Loom machines: In the weaving process, pneumatic cylinders activate the movement of the loom to maintain the quality standards of the fabric.
- Fabric cutting: Used in automatic cutting machines to enable different shapes and sizes of fabrics.
- Dyeing and printing machines: Cylindrical mechanisms ensure that the process of dyeing and printing on textiles is carried out in a smooth and repetitive manner.
7. Construction and mining:
- Excavation equipment: Cylinders are used in hammers, rock drills and other excavation equipment to move or break up material.
- Concrete pumps: These are relevant in construction to allow concrete to flow or pump in a certain direction.
- Lifting and positioning equipment: These are useful in positioning heavy equipment or materials on construction sites.
8. Aerospace industry:
- Aircraft component testing: cylinders move an aircraft component for the purpose of testing its durability.
- Assembly and maintenance: pneumatic systems achieve the desired precision when assembling aircraft parts to the required quality standard.
- Landing gear and braking systems: for some airplanes, pneumatic systems can be used for retractable landing gear and brakes.
9. Printing and Paper Industry:
- Paper Feed and Alignment: In printing machines refinishing cylinders are used to assist in the feeding, the alignment and the cutting of paper.
- Printing Press Operations: Assist in the process of applying printing pressure to maintain proper depths of impression and clear prints.
- Binding and Folding: The machines that tuck, fold and stack, and bind paper products also use pneumatic actuating systems.
Best Brand for Pneumatic Cylinder
Top Pneumatic cylinder Manufacturers in India:
1. Mercury Pneumatics
2. Janatics Pneumatic Cylinders
3. SMC Pneumatic Cylinders
4. Festo Pneumatic Cylinders
5. Nishaka Pneumatics
6. Hydro-Pneumatic Controls
7. Hydraulic & Pneumatic Products
8. A. Tech
9. Mehta Hydraulics Equipments LLP
10. Proline Industrial Valves
11. Jyoti Hydraulic
12. Honeytech Controls Pvt. Ltd
1. Karma Automation
Why Choose VS Enterprise
Choosing VS Enterprise as your partner in pneumatic solutions is the best decision, as they certainly understand the needs of the customers as the leader in the industry. This is why customers across India choose us for all their pneumatic needs:
Top Dealer of Leading Pneumatic Brands
VS Enterprise takes pride in being the main dealer of high-caliber brands such as Mercury Pneumatics, Janatics Pneumatic cylinders and Techno Pneumatic Cylinders. We concentrate on getting them genuine, high-end products from these perfect makers for their customers to get only the best in the market.
Comprehensive Product Range
Our products range covers a vast spectrum of various pneumatic parts and components which include cylinders, valves, fittings and accessories. For special pneumatic tools or standard tools, you can rely on VS Enterprise.
Industry Expertise and Experience
Our team has extensive experience and knowledge across the entire spectrum of the pneumatic industry. Understanding the nature of pneumatic systems helps us provide valuable advice on specific products used in their applications.
Unmatched Customer Support
Customer satisfaction is guaranteed at VS Enterprise. The well-trained support staff can gladly assist with product purchase and technical issues as well as after-sale services making the process much easier starting at the point of sale and continuing up until implementation.
Competitive Pricing
There are many businesses which consider quality to be expensive. However, we do not believe in that. We collaborate with eminent manufacturers in order to provide quality pneumatic products at reasonable prices.
Timely Delivery and Reliable Service
The reason why we make it a point to have a fast and effective order management and delivery process is because we know that downtime is costly for you. In working with VS Enterprise, you can be assured that your equipment will be delivered in a went state and at the right time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How can pneumatic cylinders be used as hydraulic cylinders?
Pneumatic actuators cannot directly replace hydraulic actuators, because pneumatically actuated cylinders operate at low pressures of a gas, dry air, while hydraulic cylinders operate at pressures of a fluid that are significantly higher. Nevertheless, there are some applications in light and low-pressure operations where the speed of a pneumatic actuator can be similar to that of a hydraulic cylinder.
Q2. How can I control the distance of a pneumatic cylinder?
The range of motion of a pneumatic cylinder can be controlled by manipulating the control valve, stroke limit setting or displacement sensors used to monitor and adjust travel, respectively.
Q3. Which are the best pneumatic cylinder manufacturers?
The most well-known manufacturers of pneumatic cylinders include Mercury Pneumatics, Genetics, Techno Pneumatics, SMC, Festo and Parker.
Q4. Can hydraulic cylinders be used as pneumatic cylinders?
Hydraulic cylinders are made for high-pressure liquid and pneumatic cylinders are made for compressed air. Although they are both intended to perform the same function, one should never confuse a pneumatic cylinder with a hydraulic cylinder as a pneumatic cylinder will not work on compressed air and may burst instead.
Q5. How do you reduce the speed of a pneumatic cylinder?
There are several ways to reduce the speed of a pneumatic cylinder such as the use of a flow control valve, adjustment of air pressure or the connection of a silencer.
Q6. How do you fix a pneumatic cylinder?
To successfully repair a pneumatic cylinder, the first step is to find out what went wrong (leak, incorrect speed etc.). The next step is to check the piston seals, valves and piston. While giving the final touches make sure all the replaced parts are aligned and any broken parts are replaced.
Q6. How does a pneumatic cylinder work?
A pneumatic cylinder functions by using compressed air to generate linear force. In such cases when air enters the cylinder, it exerts force on the piston located inside, causing the rod to either expand or contract depending on the direction of the air flow, which is controlled by a set of valves.


